Microservice Design Patterns: A Comprehensive Guide

Microservices architecture has become a dominant approach for building scalable and maintainable applications. Unlike monolithic architectures, microservices break applications into smaller, independently deployable services that communicate with each other. However, designing microservices effectively requires a solid understanding of various design patterns to ensure scalability, resilience, and maintainability.
In this blog, we will explore essential microservice design patterns and their significance in building robust applications.

1. Decomposition Patterns
1.1. Decomposing by Business Capability
This pattern involves breaking down services based on business functions. Each service corresponds to a specific business capability, making it easier to scale and manage. For example, in an e-commerce application, different services can handle inventory, orders, payments, and user management.
1.2. Decomposing by Subdomain (Domain-Driven Design — DDD)
Using Domain-Driven Design (DDD), microservices are decomposed based on bounded contexts, ensuring that each service has a clear and distinct responsibility.
2. Data Management Patterns
2.1. Database per Service
Each microservice manages its own database to ensure data isolation and autonomy. This prevents tight coupling but introduces challenges in data consistency.
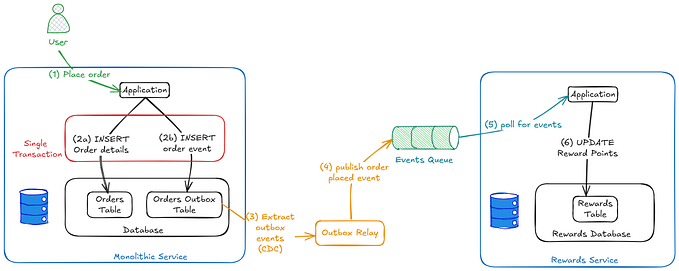
2.2. Saga Pattern
Saga pattern ensures data consistency across multiple microservices by using a sequence of distributed transactions, either in a choreography or orchestration model.
2.3. CQRS (Command Query Responsibility Segregation)
CQRS separates the read and write models, optimizing performance and scalability by using different models for querying and updating data.
3. Communication Patterns
3.1. API Gateway Pattern
An API Gateway acts as an entry point for all client requests, routing them to appropriate microservices. It helps in authentication, rate limiting, and request aggregation.
3.2. Service Mesh
A service mesh handles inter-service communication, load balancing, security, and monitoring without modifying application code. Examples include Istio and Linkerd.
3.3. Event-Driven Architecture
Microservices communicate using events instead of direct service-to-service calls. This improves scalability and decoupling.
4. Resilience and Reliability Patterns
4.1. Circuit Breaker Pattern
Prevents cascading failures by stopping requests to a failing service after a certain threshold. Netflix’s Hystrix is an example implementation.
4.2. Retry Pattern
Automatically retries failed operations with an exponential backoff strategy to improve fault tolerance.
4.3. Bulkhead Pattern
Isolates different services into separate pools to prevent failures in one service from affecting others.
5. Deployment and Observability Patterns
5.1. Sidecar Pattern
Deploys auxiliary components (e.g., logging, monitoring, or security tools) alongside microservices in the same pod or container to enhance functionality without modifying the main service.
5.2. Blue-Green Deployment
Ensures zero-downtime deployments by running two identical environments (Blue and Green) and switching traffic between them.
5.3. Centralized Logging and Monitoring
Using tools like ELK Stack, Prometheus, and Grafana helps in aggregating logs and monitoring system health.
Conclusion
Implementing microservices effectively requires adopting the right design patterns to ensure scalability, fault tolerance, and maintainability. By leveraging decomposition, data management, communication, resilience, and observability patterns, organizations can build robust and efficient microservices architectures.
Do you use microservices in your projects? Share your experiences and challenges in the comments!